IoT Security: A Must-Know Guide for Every Smart Device Owner
In this age of digital change, the Internet of Things (IoT) has emerged as a breakthrough technology. Our homes, companies, and cities have all become smarter and more effective as a result of its seamless integration into our daily lives. However, the issues that come with living in a connected society mostly revolve around IoT security vulnerabilities. In this article, we will delve into the intricate web of IoT security concerns, exploring their implications and offering insights on how to protect against them.
Understanding the Basics
What is IoT?
IoT refers to the network of interconnected physical devices, vehicles, buildings, and other objects that collect and exchange data through embedded sensors and communication interfaces. These devices can include everything from smart thermostats and wearable fitness trackers to industrial machinery and automobiles.
Why is IoT Security Crucial?
Ensuring the security of IoT devices and networks is paramount because they often handle sensitive data and control critical systems. Breaches can lead to privacy violations, financial losses, and even physical harm.
Unveiling the IoT Security Gaps

Weak Passwords
Many IoT devices come with default passwords, leaving them susceptible to malicious attacks. Users often overlook the importance of setting unique and strong passwords. Weak passwords are like leaving your front door unlocked in a busy neighborhood. Cybercriminals can quickly exploit IoT security vulnerability to gain unauthorized access to your IoT devices, compromising on your privacy and security. To mitigate this risk, it’s crucial to change default passwords to strong, unique combinations. Utilize a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) wherever possible. MFA adds an extra layer of IoT security by requiring users to provide two or more forms of verification before gaining access. Further more if you want to know about most critical vulnerabilities identified in 2023, click here.
Outdated Firmware
Manufacturers may not regularly update the firmware of IoT devices, leaving IoT security with vulnerabilities to known exploits. This gap in IoT security maintenance is a significant concern.
Firmware is the software that runs on IoT devices. Just like your computer’s operating system, firmware needs regular updates to patch vulnerabilities and enhance IoT security. However, some manufacturers do not provide timely updates, leaving their devices exposed to new arriving threats.
To address this issue, keep a close eye on firmware updates for your IoT devices. Manufacturers typically provide instructions on how to check for and apply these updates in the device’s manual or on their website. Regularly updating your devices’ firmware is an essential step in safeguarding your IoT ecosystem. You know outdated MAC OS is also vulnerable to cybercriminals, Don’t you? Click here.
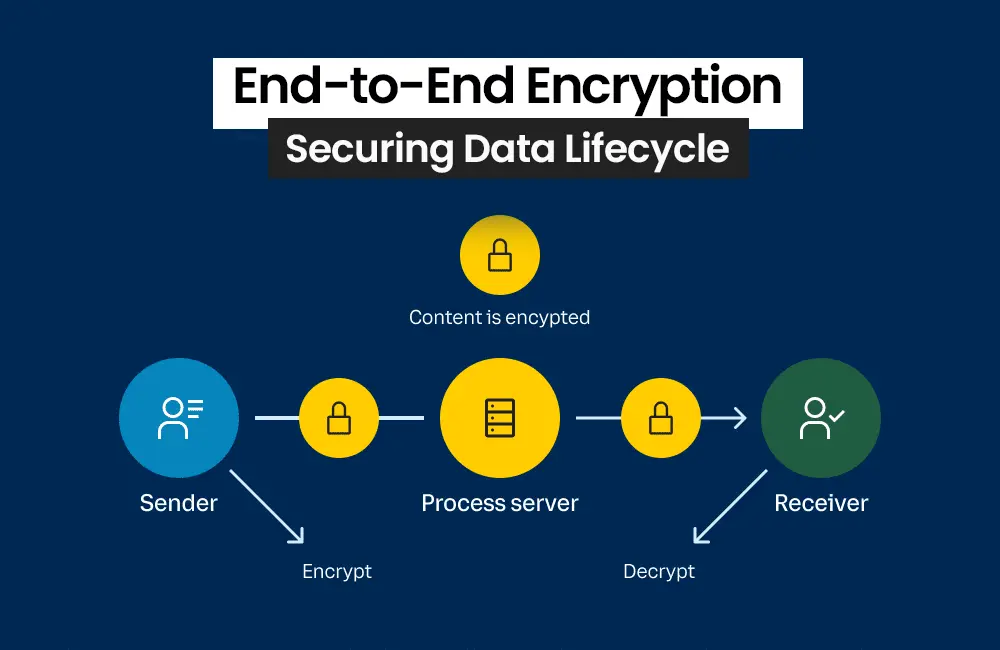
Inadequate Encryption
Sensitive data is more easily stolen and misused by cybercriminals when there is weak encryption used during data transfer. Encryption transforms into a code data to prevent unauthorized access. It makes sure that information sent between IoT devices and the network is safe and cannot be readily intercepted or altered with IoT security breach.
Make sure your IoT devices use strong encryption protocols like Transport Layer Security (TLS) or Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) to increase encryption in your IoT ecosystem. These protocols offer a secure route for data transmission, making it far more difficult for hackers to intercept or interfere with the data.
Lack of Authentication
Some IoT devices lack proper user authentication, making it possible for unauthorized individuals to gain access to them. Authentication is verifying the identity of a user or device before granting access. In IoT, it ensures that only allowed users can control and access devices. When IoT devices lack authentication measures, anyone with access to the network might manipulate or control them.
To enhance authentication in your IoT security and setup, consider implementing strong authentication methods, such as biometric recognition, smart cards, or unique device-specific keys. These measures ensure that only allowed individuals can interact with your IoT devices.
Poorly Designed APIs
Weak Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) and weak IoT security can be exploited to gain control over IoT devices, leading to IoT security breaches. APIs are the communication channels that allow different software components to interact. In IoT, they enable applications to communicate with and control IoT devices. Weak or poorly designed APIs can be an open invitation to cybercriminals looking for vulnerabilities.
To address this concern, device manufacturers need to prioritize secure API design. Users should also be cautious when granting applications access to their IoT devices. Only allowed and trusted applications can review and revoke permissions for applications that are no longer needed.
The Implications of Vulnerabilities

Privacy Breaches
Unauthorized access to IoT devices can lead to compromise personal information, such as home security camera footage or health data from wearable devices. Privacy breaches in the IoT realm deeply concern. Imagine an unauthorized individual gaining access to your smart home security cameras, allowing them to monitor your daily activities. Such breaches put your physical security at risk by violating your privacy.
Protecting your privacy involves implementing strong IoT security practices, as mentioned earlier. Regularly review the permissions and access levels of your IoT devices to ensure that only authorized users can access sensitive data. OploxTech is the company who is providing most updated and with fewer vulnerabilities to cyber criminals. A trustworthy company to develop website and/or mobile application for your business
Botnet Attacks
Cyber criminals can harness vulnerable IoT devices to create massive botnets capable of launching Distributed Denial of Service (DoS) attacks on websites and networks. Botnets are armies of compromised IoT devices controlled by malicious actors. They can overwhelm websites and networks with traffic, rendering them inaccessible. IoT devices, if not properly secured, can become unwitting members of these botnets.
To prevent your IoT devices from being recruited into a botnet, ensure that they are updated with the latest firmware and have stronger IoT security configurations. Network segmentation, isolating IoT devices from critical systems, can also prevent them from being used in botnet attacks.
Critical Infrastructure Threats
Inadequate IoT security in industrial systems can jeopardize critical infrastructure, leading to disruptions in essential services like energy and transportation. Industrial IoT is a subset of IoT that focuses on industrial applications, including manufacturing, energy management, and transportation. Compromised IoT systems can lead to catastrophic failures with far-reaching consequences.
Securing IoT devices involves rigorous IoT security audits, intrusion detection systems, and robust access controls. Industrial facilities should prioritize IoT security as an integral part of their operations to protect against potential threats.
Safeguarding Your IoT Ecosystem

The vulnerabilities in IoT security are real and significant, but they can be mitigated through proactive measures. Here are some steps to safeguard your IoT ecosystem:
1. Strong Passwords and Authentication
Always change default passwords, use complex combinations, and enable multi-factor authentication wherever possible.
2. Regular Firmware Updates
Check for firmware updates and apply them promptly to patch known vulnerabilities.
3. Network Segmentation
Isolate IoT devices on a separate network to prevent unauthorized access to more critical systems.
4. Encryption
Ensure that data transmitted between IoT devices and the network is encrypted using robust protocols.
5. IoT Security Audits
Periodically assess the security of your IoT ecosystem and address any weaknesses promptly.
Conclusion
IoT security vulnerabilities are a stark reality in our interconnected world. Understanding these vulnerabilities and taking proactive measures to mitigate them is crucial to safeguarding our privacy, data, and critical infrastructure. By adopting robust IoT security practices, we can harness the full potential of IoT while minimizing the associated risks.