Cyber Threat Prevention: How to Identify & Avoid Phishing Attack?
Phishing is a deceptive cyber-attack technique used by malicious actors to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, credit card details, or personal identification. This is typically done through fraudulent emails, messages, malware URL, or websites that impersonate trustworthy entities.
The Anatomy of a Phishing Attacks

Phishing attacks usually follow a specific structure. They begin with a lure, such as an enticing email or message, and then attempt to hook the victim by convincing them to take a particular action. This action often involves disclosing personal information or downloading malicious attachments. These scams typically follow a specific pattern:
1. The Lure:
Phishing attack starts with a lure, which could be an email, message, or even a phone call. This initial contact is designed to pique your curiosity or create a sense of urgency.
2. False Pretenses:
Phishers often impersonate trusted entities like banks, government agencies, or well-known companies. They may claim that your account is compromised or that you’ve won a prize to grab your attention.
3. The Hook:
The scam hinges on convincing you to take a specific action. This could be clicking a malware link, downloading an attachment, or providing sensitive information like passwords or credit card details.
4. Concealing Malicious Intent:
Phishers go to great lengths to hide their malicious intent and the malware. They might use legitimate-looking logos, email addresses, or website designs to appear genuine.
5. Exploiting Human Psychology:
Social engineering techniques play a significant role in phishing attack. Phishers use psychological manipulation to create fear, curiosity, or trust to deceive victims.
6. Escalating Consequences:
Emails for phishing attack often escalate consequences if you don’t act immediately. They may threaten to close your account or report you for legal issues while playing a psychological malware game.
Common Types of Phishing Attacks
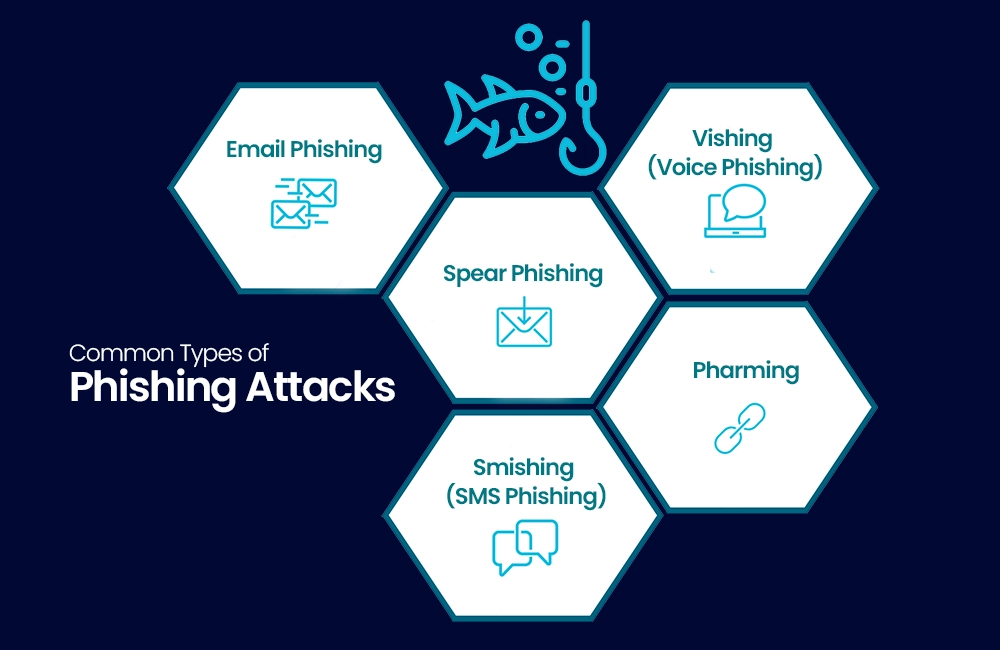
There are several types of phishing attacks, each with its own modus operandi. Understanding these variations is crucial in preventing them.
1. Email Phishing Attack:
Email phishing attack is the most common type of phishing attack. It involves deceptive emails that appear to come from legitimate sources, such as banks or government agencies. These emails often contain malware, links that lead to fake websites designed to steal your login credentials.
2. Spear Phishing Attack:
Spear phishing attack is a targeted form of phishing. Attackers research their victims and craft personalized messages to increase the likelihood of success. It is commonly used against high-profile individuals or within organizations.
3. Vishing (Voice Phishing Attack):
Vishing involves phishing attack through voice communication. Scammers make phone calls, often pretending to be from a trusted organization, and attempt to extract personal information or money from their victims.
4. Smishing (SMS Phishing):
Smishing is like email phishing attack but uses SMS or text messages to deceive recipients. These messages contain malware, links or phone numbers that, when contacted, lead to scams.
5. Pharming:
Pharming is a more sophisticated attack where cybercriminals manipulate the DNS system to redirect users to fake websites, even if they type the correct URL into their browsers. For more information and to have penetration testing, follow us on LinkedIn.
Recognizing Phishing Emails

Identifying phishing emails is crucial to protecting yourself from these scams. Here are some common signs to look out for:
1. Generic Greetings:
Phishing emails with malware links or content often begin with generic greetings like “Dear User” or “Hello Customer” instead of addressing you by name.
2. Urgent or Threatening Language:
Phishers use urgency and threats to pressure you into taking immediate action. They may claim your account will be closed or legal action will be taken if you don’t comply.
3. Spelling and Grammar Mistakes:
Many phishing emails contain spelling and grammatical errors. Legitimate organizations usually maintain a higher level of professionalism in their communications.
4. Mismatched URLs:
Check the sender’s email address and the URLs in the email. Phishers often use slight variations of legitimate addresses to trick recipients.
5. Requests for Personal Information:
Be cautious if an email requests sensitive information like passwords, Social Security numbers, or credit card details.
6. Unsolicited Attachments or Links:
Avoid opening attachments or clicking links in suspicious emails. These may contain malware or lead to phishing websites.
Suspicious URLs: A Red Flag

The URLs in email for phishing attack often serve as a red flag. Here’s how to identify suspicious URLs:
1. Check the Domain:
Examine the domain name in the URL. Phishing sites may use domains that look similar to legitimate ones but contain slight misspellings or added characters.
2. Look for HTTPS:
Legitimate websites use HTTPS for secure connections. If the site doesn’t have HTTPS, be cautious. This could be a malware.
3. Inspect the Path:
Review the path in the URL. Phishing URLs may have unusual paths or long strings of characters.
4. Beware of Malware Pop-Ups:
If a pop-up prompts you to enter personal information, it’s likely a phishing attempt.
5. Hover Over Links:
Hover your cursor over links without clicking to see the actual URL. Ensure it matches the expected destination.
The Role of Social Engineering

Social engineering is a psychological manipulation technique used by phishers to deceive their victims. It involves tactics that exploit human psychology, creating a false sense of trust or urgency. Here are some common social engineering tactics used in phishing attack:
1. Fear and Intimidation:
Phishers create a sense of fear or urgency to pressure victims into taking immediate action making click on malware link. They may threaten account suspension, legal consequences, or financial loss.
2. Curiosity:
Some phishing emails pique curiosity by promising rewards, prizes, or exclusive content. The desire to explore what’s behind the message can lead to victimization.
3. Trust and Authority:
Phishers often impersonate trusted organizations, government agencies, or colleagues. They exploit the trust you have in these entities to manipulate you.
4. Reciprocity:
Some scams offer a small favor or gift in exchange for personal information. This plays on the principle of reciprocity, where people feel obligated to give something in return.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)

Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is an effective way to enhance the security of your online accounts. It requires users to provide two or more verification factors before gaining access. Here’s how to set up MFA:
1. Choose a Trusted MFA Method:
Select a reliable MFA method, such as a one-time code sent via text message, an authentication app, or a hardware token.
2. Enable MFA:
Access your account settings and enable MFA. Follow the provided instructions to link your chosen method.
3. Verification Process:
When logging in, you’ll be prompted to provide the second factor, which is typically a code generated by your chosen method. Also read about the bundle of other cybersecurity topics by clicking here.
Reporting Phishing Attacks

Reporting malware links and phishing attacks is a responsible step in preventing further attacks and helping authorities take action against cybercriminals. Here’s how to report a phishing attacks:
1. Contact Anti-Phishing Organizations:
Reach out to organizations like the Anti-Phishing attack Working Group (APWG) or the Cybercrime Support Network. They specialize in handling phishing reports.
2. Forward Suspicious Emails:
If you receive a phishing email, forward it to the Anti-Phishing organizations or your organization’s IT department.
3. Provide Details:
Include as many details as possible when reporting, such as the email’s content, sender’s address, and any suspicious URLs.
The Consequences of Falling for Phishing Attacks

The consequences of falling for phishing attacks can be severe and far-reaching. It’s crucial to be aware of the potential outcomes to motivate vigilance and caution. Here are some of the common consequences:
1. Financial Loss:
Phishing attacks can lead to unauthorized transactions, drained bank accounts, or fraudulent credit card charges.
2. Identity Theft:
Scammers may use the stolen information to commit identity theft, leading to long-lasting financial and legal issues.
3. Unauthorized Account Access:
Once phishers have your login credentials, they can access your accounts, change passwords, and lock you out.
4. Malware Infections:
Clicking on malicious links or downloading attachments can infect your device with malware, potentially compromising your personal data.
5. Reputation Damage:
Falling for phishing attacks can damage your reputation, especially if scammers use your email or social media accounts for further scams.
Conclusion
In an age where digital attacks are on the rise, it’s crucial to stay informed and vigilant against phishing attacks. By recognizing the signs and taking preventive measures, you can protect your personal information and ensure a safer online experience.