How to Boost Business Protection Against AI-Powered Cybercrime
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, businesses navigate a minefield of modern challenges, with the specter of cybercrime looming large. With integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) into malevolent activities, a new era of cybercrime has dawned. For businesses, understanding and mitigating the risks associated with cybercrime are paramount to ensuring the longevity of their operations, the safety of sensitive data, and the preservation of their reputation.
Understanding AI-Powered Cybercrimes

Defining AI-Powered Cybercrimes
In the realm of “cybercrime,” AI-powered threats have become the new norm. These sophisticated cyber threat activities harness the capabilities of AI and machine learning to infiltrate systems, exploit vulnerabilities, and compromise the security of businesses. Recognizing the multi-faceted nature of these AI-driven cybercrime activities is an essential step towards effective defense.
The Threat Landscape
The digital landscape is replete with potential threats, and cybercrime stands out as a formidable adversary. AI-powered cybercrime tactics have elevated the complexity and adaptability of threats, making it crucial for businesses to remain vigilant in the face of these ever-evolving challenges. if you want to know about cyber vulnerabilities identified in 2023 then click here.
Common AI-Powered Cybercrime Techniques

Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks, traditionally recognized as a form of “cybercrime,” have taken a quantum leap with AI’s infusion. These AI-driven activities craft highly convincing and targeted messages, making it increasingly challenging to detect and protect against such deceptions.
Ransomware
Ransomware, known for its disruptive cybercrime potential, now exploits AI for enhanced adaptability. AI-powered ransomware can circumvent security measures, substantially raising the stakes for businesses dealing with this form of “cybercrime.”
Deepfakes
“Deepfake” technology, empowered by AI, poses a novel challenge in the fight against “cybercrime.” It has the ability to fabricate incredibly convincing audio and video content, creating ample opportunities for cybercriminals to deceive individuals and organizations.
Social Engineering
AI’s role in cyberattacks extends to social engineering tactics. By scrutinizing voluminous social media data, AI can concoct personalized, persuasive messages, a hallmark of modern cybercrime strategies.
The Vulnerabilities in Business Systems

Legacy Systems
Legacy systems, often ripe for cybercrime exploitation, lack up-to-date security features, making them inviting targets for AI-powered attacks. Businesses must identify and address these vulnerabilities to ensure robust security measures.
Lack of Employee Training
Inadequate employee training is a weak link in the defense against cyber threats. AI-fueled cybercrime tactics can confound untrained employees, emphasizing the need for continuous education and vigilance. If you want to be prepared to secure yourself from XSS Attacks then click here.
Inadequate Security Protocols
Weak or outdated security protocols create vulnerabilities that cybercriminals are all too eager to exploit. Fortifying these protocols is essential for safeguarding against cybercrime.
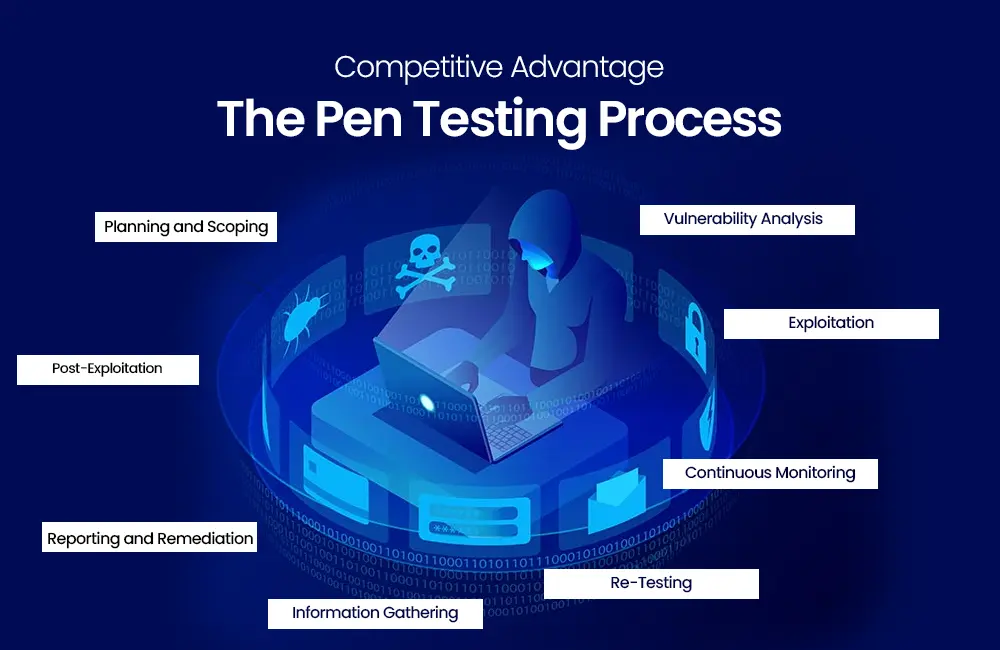
Steps to Boost Business Protection

Keep Software Up to Date
Regularly updating software and applying security patches is the cornerstone of cybercrime protection. This routine maintenance ensures that systems remain resilient against emerging cyber threats.
Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA introduces an extra layer of cyber defense. By requiring multiple verification steps it significantly elevates the complexity of gaining unauthorized access, even if cybercriminals get one set of credentials.
Conduct Regular Security Audits
Regular cybercrime audits play a crucial role in identifying system weaknesses. This proactive approach enables businesses to mitigate vulnerabilities before they are exploited, enhancing overall security.
Employee Training and Awareness
Employee education is pivotal in cyber defense. Well-informed employees are the first line of protection against AI-driven cyber threats. Promoting awareness and vigilance among staff is an effective cybercrime deterrent.
The Role of AI in Cybersecurity

AI-Powered Threat Detection
In the battle against cyber threats AI plays a pivotal role in early threat detection. AI can analyze extensive datasets in real-time, enabling rapid response to potential cybercrime incidents, thereby reducing potential damage.
Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics, driven by AI, forecast potential cyber threats. By scrutinizing historical data and patterns, AI facilitates a proactive approach to cybercrime protection.
Automated Incident Response
AI’s automated response to security incidents is a game-changer in cyber defense. Swift and efficient, this response minimizes potential damage during cybercrime incidents.
Collaboration with Cybersecurity Experts

Outsourcing vs. In-House Expertise
The decision between outsourcing cybersecurity and maintaining an in-house team is a critical aspect of cyber defense. Factors like an organization’s specific cybersecurity needs, available resources, and budget influence this choice. Get our expert cybersecurity services from cybernexguard.com
Investing in Cybersecurity Tools

Firewalls and Antivirus Software
Traditional cybersecurity tools remain fundamental in the fight against “cybercrime.” Firewalls and antivirus software offer robust cybercrime protection against various threats.
Intrusion Detection Systems
Advanced AI-driven intrusion detection systems are pivotal in cybercrime detection. These systems identify unusual or suspicious activities within a network, a key feature in comprehensive cyber defense.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Solutions
SIEM solutions, through their analysis of security data, provide a holistic view of potential cyber threats and vulnerabilities. SIEM is an indispensable component of cybersecurity. For more information and other services, follow us on Facebook, Instagram, and LinkedIn.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance

GDPR and Data Protection
Compliance with regulations such as GDPR is not just about legal consequences; it also protects individual data privacy rights. Businesses must adhere to legal standards for data protection to safeguard against cybercrime and maintain trust.
Industry-Specific Regulations
Diverse industries may have specific cybercrime regulations tailored to their unique risks and challenges. Comprehending and adhering to these industry-specific cybercrime regulations is crucial for businesses’ security and compliance.
Building a Cybersecurity Culture

From Top to Bottom
A cybercrime resilient culture should begin at the highest levels of an organization. When leaders prioritize and model security best practices, they set a strong foundation for cyber defense.
Reporting Mechanisms
Establishing clear and confidential channels for reporting suspicious activities empowers employees to participate in the organization’s cybersecurity. A culture of reporting acts as a powerful deterrent against AI-powered cyberattacks.
Consequences for Non-Compliance
Introducing consequences for non-compliance with security protocols motivates employees to take cybersecurity seriously. A culture of accountability reinforces the importance of adhering to best practices and fosters a secure environment.
Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation

The Dynamic Nature of Cyber Threats
The ever-evolving landscape of cyberattack necessitates continuous monitoring. AI-powered cyber threats adapt rapidly, making ongoing vigilance vital for staying ahead of cybercrime activists.
Staying One Step Ahead
Proactive monitoring and adaptive security measures enable businesses to outpace cybercriminals. This forward-thinking approach is a linchpin of cyber defense, ensuring the safety of sensitive data and operations.
Case Studies
Successful Business Protection Against AI-Powered cyberattack
Analyzing real-world cases of businesses successfully thwarting AI-powered cybercrime incidents provides invaluable insights and inspiration for organizations seeking to enhance their cybersecurity measures.
Measuring the ROI of Cybersecurity

Tangible vs. Intangible Benefits
Evaluating the return on investment in cybersecurity encompasses both measurable benefits, such as cost savings and risk reduction, as well as intangible benefits like improved reputation and customer trust. A holistic assessment is essential for organizations aiming to understand the full scope of their cyber defense efforts.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the ascent of AI-powered cyberthreats highlights the necessity for businesses to adopt proactive measures to fortify their defenses. Understanding the dynamic threat landscape, implementing comprehensive security measures, and fostering a cybersecurity culture are instrumental steps in mitigating the risks posed by AI-driven cybercrime activities.