How to Keep Mac Safe with macOS Ventura 13.3 Security Update
In the ever-evolving digital landscape, ensuring the security of your Mac is of paramount importance. With the release of macOS Ventura 13.3, Apple has introduced significant security enhancements to safeguard your device and data. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore how to keep your Mac safe with the macOS Ventura 13.3 Security Update. From understanding the latest security features to implementing best practices, we’ve got you covered.
Introduction to macOS Ventura 13.3 Security Update
macOS Ventura 13.3 brings a host of new security features and enhancements designed to protect your Mac from evolving threats. Whether you use your Mac for work, leisure, or both, these updates are vital to keeping your data and privacy secure. With the growing sophistication of cyber threats, it has become more important than ever to stay one step ahead. Apple recognizes this and has made it a priority to fortify the security of its operating system.
Why Security Updates Are Crucial
Security updates are not mere software upgrades; they are your shield against the latest vulnerabilities and exploits. Staying up to date ensures that your Mac is equipped to defend against emerging threats.
Cybercriminals are constantly devising new methods to infiltrate systems and steal sensitive information. Without regular security updates, your Mac could be susceptible to these threats.
macOS Ventura 13.3’s security update is designed to patch known vulnerabilities and strengthen the system’s defenses. By neglecting these updates, you’re essentially leaving the door open for potential attacks. To read more about cybersecurity vulnerabilities and their solutions in 2023 please click here.
Checking for Updates
Before diving into the macOS Ventura 13.3 Security Update, it’s essential to verify if your system is due for an update. Apple regularly releases updates, so keeping an eye on these is crucial.
To check for updates:
1. Click on the Apple menu in the top-left corner of your screen.
2. Select “About This Mac.”
3. Click on the “Software Update” button.
If there are updates available, you will be prompted to download and install them. Ensure your Mac is connected to the internet to receive the latest updates.
Installing macOS Ventura 13.3

Updating your Mac to macOS Ventura 13.3 is a straightforward process. We’ll walk you through the steps to ensure a smooth transition and enhanced security.
1. Backup Your Data: Before performing any major system update, it’s wise to back up your data. You can use Time Machine or other backup solutions for this purpose.
2. Connect to a Stable Network: Ensure that your Mac is connected to a stable and reliable Wi-Fi network. Interrupted downloads can lead to incomplete installations.
3. Check Storage Space: Make sure you have sufficient free space on your Mac’s hard drive to accommodate the update. macOS updates can be quite large.
4. Download and Install:
- Go to the Apple menu and select “About This Mac.”
- Click on the “Software Update” button.
- If macOS Ventura 13.3 is available, click “Upgrade Now” to begin the download.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation.
Once the installation is complete, your Mac will restart, and you’ll be running the latest version with enhanced security features.
Enhanced Password Management
Your passwords are your first line of defense. Learn how to manage your passwords effectively and ensure that they are strong and unique.
Use a Password Manager
One of the most significant security risks is using weak, easily guessable passwords or reusing them across multiple accounts. A password manager can generate and store complex, unique passwords for each of your accounts, making it virtually impossible for attackers to crack them.
Enable iCloud Keychain
Apple’s iCloud Keychain securely stores your passwords and syncs them across your Apple devices. It can also suggest strong, unique passwords when you create new accounts.
Regularly Update Passwords
Make it a habit to update your passwords periodically. If a service you use is breached, changing your password immediately can prevent unauthorized access.
Adding an extra layer of security to your Apple ID can prevent unauthorized access. We’ll show you how to enable and use Two-Factor Authentication.
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)

Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) requires you to provide two forms of identification before accessing your account. In addition to your password, you’ll receive a verification code on your trusted device, such as your iPhone, which you’ll need to enter to log in.
To enable 2FA on your Apple ID:
- Go to “Settings” on your iPhone or iPad.
- Scroll down and tap “Password & Security.”
- Tap “Turn On Two-Factor Authentication.”
Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the setup. Once enabled, your Apple ID will be significantly more secure.
Secure Boot Process
Understanding the secure boot process is essential for ensuring the integrity of your system’s software. We’ll explain how it works and why it’s vital.
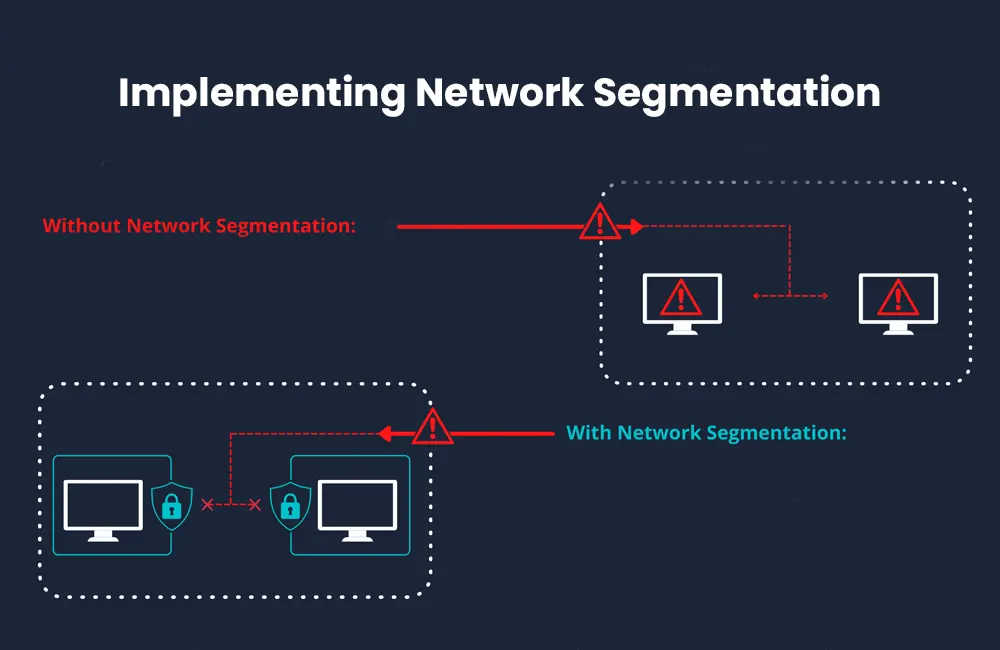
The secure boot process ensures that only trusted software is loaded during startup. This prevents malware and unauthorized modifications from taking control of your Mac.
macOS Ventura 13.3 enhances the secure boot process by incorporating the latest cryptographic standards and technologies. When you power on your Mac, the firmware performs checks to ensure that the bootloader, kernel, and essential system files haven’t been tampered with.
If any discrepancies are detected, your Mac will refuse to boot, protecting your system from potential threats.
App Permissions and Privacy Controls
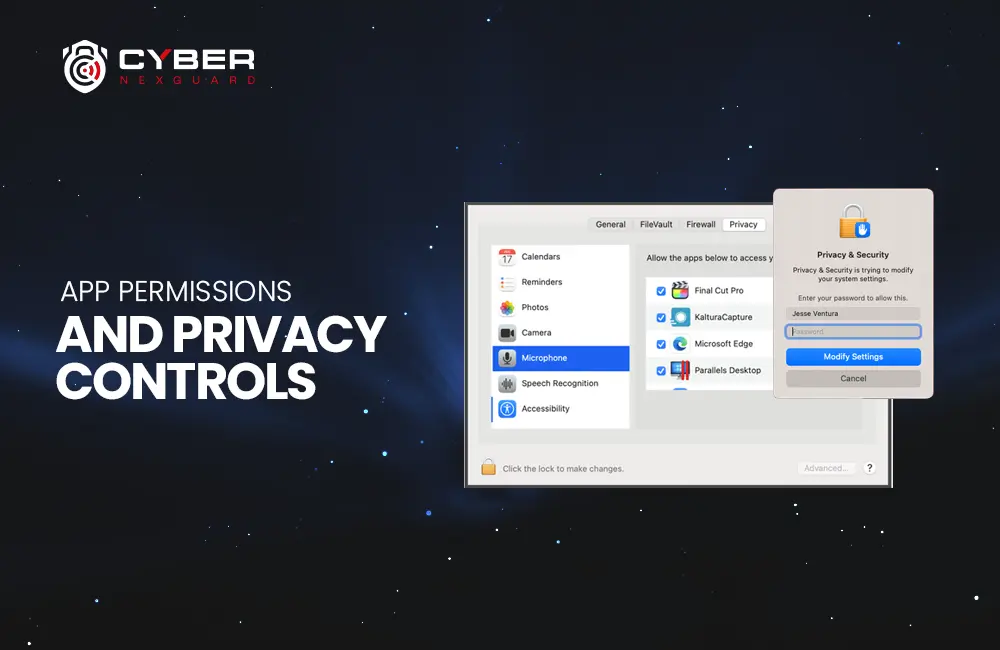
Control over your apps’ permissions and data access is critical. Discover how to manage these settings effectively.
Review App Permissions
macOS Ventura 13.3 introduces improved app permission management. When you install a new app, it will request access to specific features or data. Review these requests carefully and grant only the necessary permissions.
Monitor Location Services
Some apps may request access to your location. While this can be useful, it’s important to review which apps have this access and disable it for apps that don’t need it.
Limit Access to Contacts
Similarly, you can control which apps have access to your contacts. Protecting your contact list can prevent unauthorized access to your personal network.
Built-in Firewall
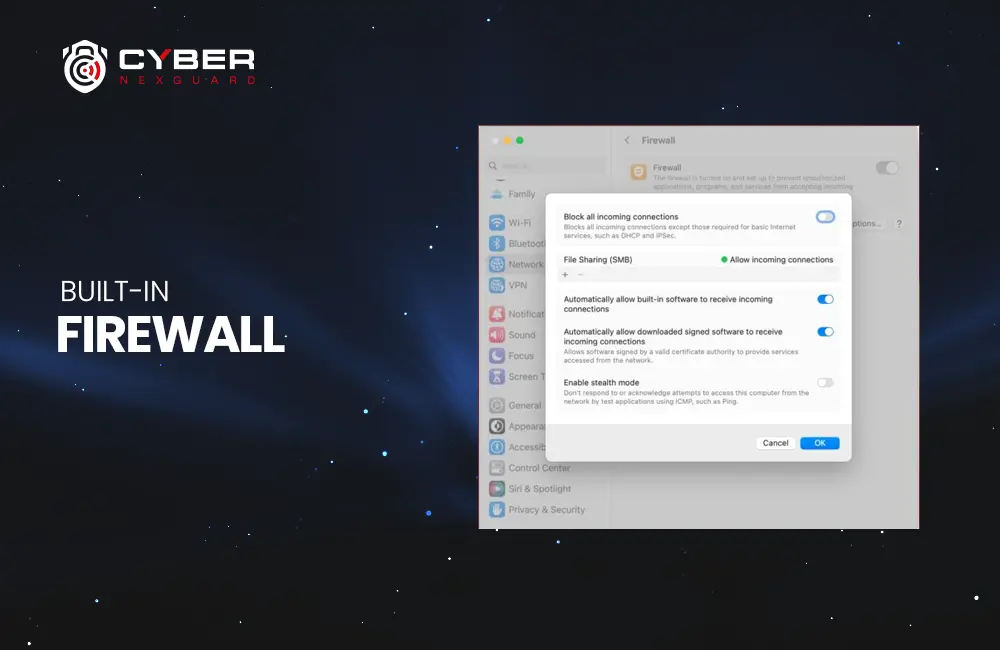
macOS Ventura 13.3 includes a built-in firewall. Learn how to configure it to protect your Mac from incoming threats.
A firewall acts as a barrier between your Mac and potential threats from the internet. It monitors incoming and outgoing network traffic and blocks suspicious activity.
To configure the built-in firewall:
- Go to “System Preferences” from the Apple menu.
- Click on “Security & Privacy.”
- Select the “Firewall” tab.
- Click the lock icon in the bottom-left corner and enter your administrator password.
- Click “Turn On Firewall.”
You can also click “Firewall Options” to customize the firewall’s settings further.
Safari Security Improvements

Safari, your default web browser, receives updates to enhance your browsing security. We’ll explore these improvements and how they benefit you.
Apple continually improves Safari’s security features to protect you while browsing the web. Some of the enhancements in macOS Ventura 13.3 include:
- Intelligent Tracking Prevention: Safari prevents websites from tracking your online behavior without your consent.
- Password Monitoring: Safari will alert you if it detects that a password you’ve used has been compromised in a data breach.
- Enhanced Privacy Report: You can view a privacy report that shows how websites you visit treat your privacy.
These features collectively provide a safer browsing experience by minimizing the risk of tracking and data breaches.
Anti-Phishing Measures

Phishing attacks are prevalent, but with macOS Ventura 13.3, you gain additional safeguards against them. We’ll explain how to recognize and avoid phishing attempts.
Phishing is a deceptive practice where attackers try to trick you into revealing sensitive information, such as passwords or credit card details. macOS Ventura 13.3 includes anti-phishing measures to help you stay safe.
Be Wary of Suspicious Emails
Phishing often starts with an email that appears to be from a legitimate source, such as a bank or online service. Be cautious when receiving emails asking for personal or financial information.
Verify URLs
Before clicking on any links, hover your mouse over them to preview the destination URL. Ensure that it matches the legitimate website’s domain.
Use Safari’s Anti-Phishing Features
Safari in macOS Ventura 13.3 has improved anti-phishing capabilities. It will warn you if you visit a website known for phishing attempts.
Stay Informed
Stay updated on the latest phishing tactics and educate yourself about how to recognize phishing attempts.
Safe Downloading Practices

Downloading files from the internet can be risky. We’ll provide tips on how to download safely and avoid malware.
Download from Trusted Sources
Whenever possible, download software and files from official websites or reputable app stores like the Mac App Store. Avoid downloading cracked or pirated software.
Check File Signatures
macOS Ventura 13.3 introduces enhanced file signature checking. This feature verifies that downloaded files haven’t been tampered with or infected with malware.
Use Safari’s Downloads Feature
When downloading files through Safari, it will check the safety of the file and notify you if it’s potentially harmful.
Regularly Update Software
Keep all your software, including your web browser and plugins, up to date. Software updates often include security patches to address known vulnerabilities.
Protecting Personal Data

Your personal data is valuable. We’ll show you how to take extra precautions to protect it from prying eyes.
FileVault Encryption
macOS Ventura 13.3 includes FileVault, which encrypts your entire hard drive. In the event of theft or unauthorized access, your data remains protected.
To enable FileVault:
- Go to “System Preferences” from the Apple menu.
- Click on “Security & Privacy.”
- Select the “FileVault” tab.
- Click the lock icon in the bottom-left corner and enter your administrator password.
- Click “Turn On FileVault.”
Manage App Permissions
Review the permissions granted to apps on your Mac. Disable access to sensitive data unless it’s necessary for the app to function. For development of trustworthy and flawless iOS mobile applications you can visit here.
Use Strong Passwords
Always use strong, unique passwords for your accounts. Avoid using easily guessable information like birthdays or common phrases.
Educate Yourself
Stay informed about common scams and data breaches. Knowledge is a powerful tool in protecting your personal information.
Security for iCloud Services
iCloud is an integral part of the Apple ecosystem. Learn about the security enhancements for iCloud services and how to maximize their protection.
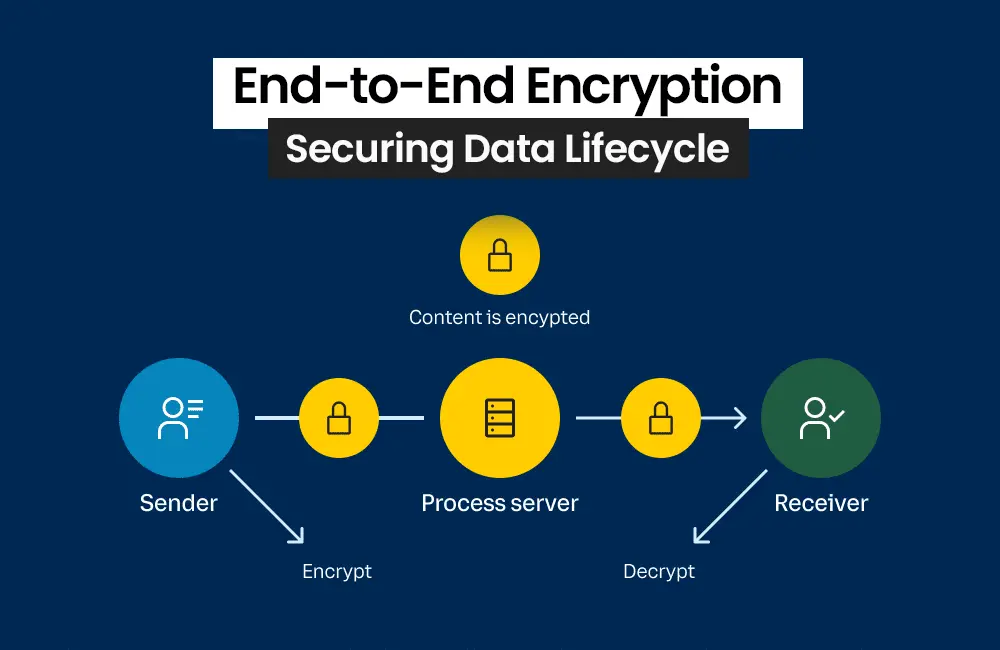
iCloud secures your data, including photos, documents, and backups. With macOS Ventura 13.3, Apple has strengthened iCloud security with features such as end-to-end encryption for iCloud backups.
To maximize iCloud security:
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication: We’ve already discussed the importance of 2FA. Enable it for your Apple ID to add an extra layer of security to your iCloud data.
- Use Strong iCloud Password: Your iCloud password should be strong and unique. Avoid using the same password for your iCloud account as you do for other accounts.
- Regularly Review Connected Devices: Periodically review the devices connected to your iCloud account. Remove any that you no longer use or recognize.
A Secure Mac for Peace of Mind
In conclusion, macOS Ventura 13.3 Security Update empowers you to take control of your Mac’s security. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can enjoy a safer and more secure digital experience.
By regularly updating your system, managing your passwords effectively, enabling Two-Factor Authentication, and practicing safe online habits, you can minimize the risk of falling victim to cyber threats.
Your Mac is an essential part of your daily life, and it’s worth investing the time and effort to keep it secure.