How to Boost Cloud Computing Security Against Vulnerabilities
In the age of digital transformation, cloud computing has emerged as a game-changer for organizations of all sizes. It offers unmatched scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency, making it an attractive option for businesses to store, manage, and process their data and applications. However, as the adoption of cloud services grows, so do the risks associated with cloud computing. In this blog, we will delve into the world of cloud vulnerabilities, exploring the various threats and challenges that organizations face when they entrust their data to the cloud.
Understanding Cloud Computing

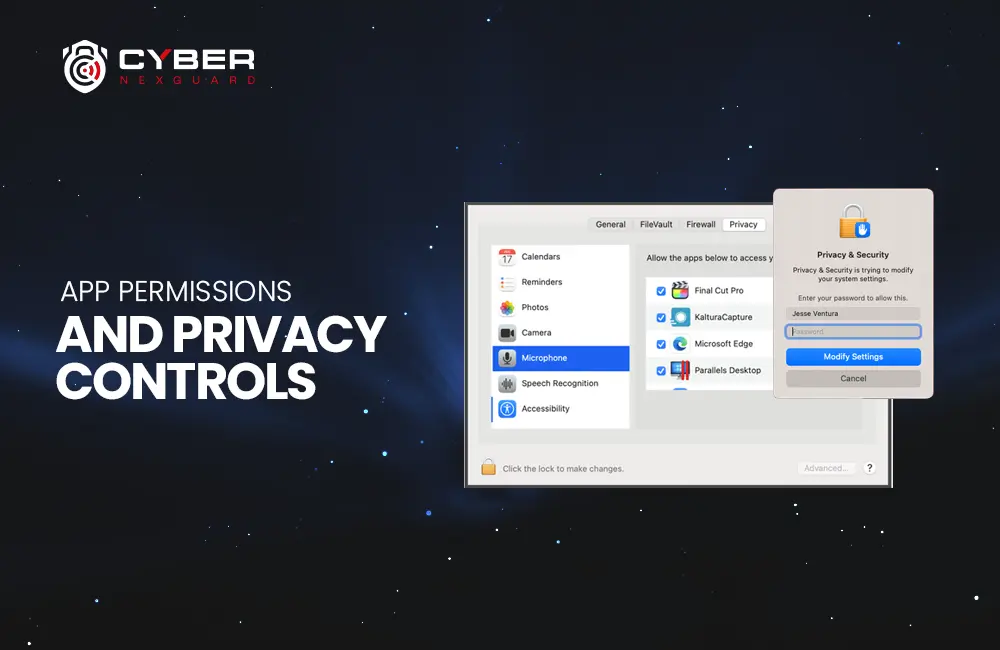
Before we delve into cloud vulnerabilities, let’s briefly understand what cloud computing is. Cloud computing involves the delivery of computing services over the internet, enabling users to access and use resources such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and more without owning or maintaining the physical infrastructure. Cloud service providers (CSPs) like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) typically provide these services. Users can choose from various service models, including Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaSa), and Software as a Service (SaaS), depending on their needs. if you want to get knowledge about vulnerabilities in Mac OS (iOS), click here.
Types of Cloud Computing Deployments

Cloud deployments can be categorized into three main types:
Public Cloud:
Services are provided by third-party CSPs and are accessible to anyone over the internet. Examples include AWS, Azure, and GCP.
Private Cloud:
A single organization uses exclusively resources. They can be hosted on-premises or by a third-party provider. Private clouds offer greater control but may be costlier.
Hybrid Cloud:
Combines elements of both public and private clouds, allowing data and applications to be shared between them. This offers flexibility but also introduces complexities in terms of security and management.
Cloud Vulnerabilities: The Risks in Cloud Computing
Understanding vulnerabilities cloud is essential for making informed decisions and implementing robust security measures in the ever-expanding realm of cloud computing.
Data Breaches
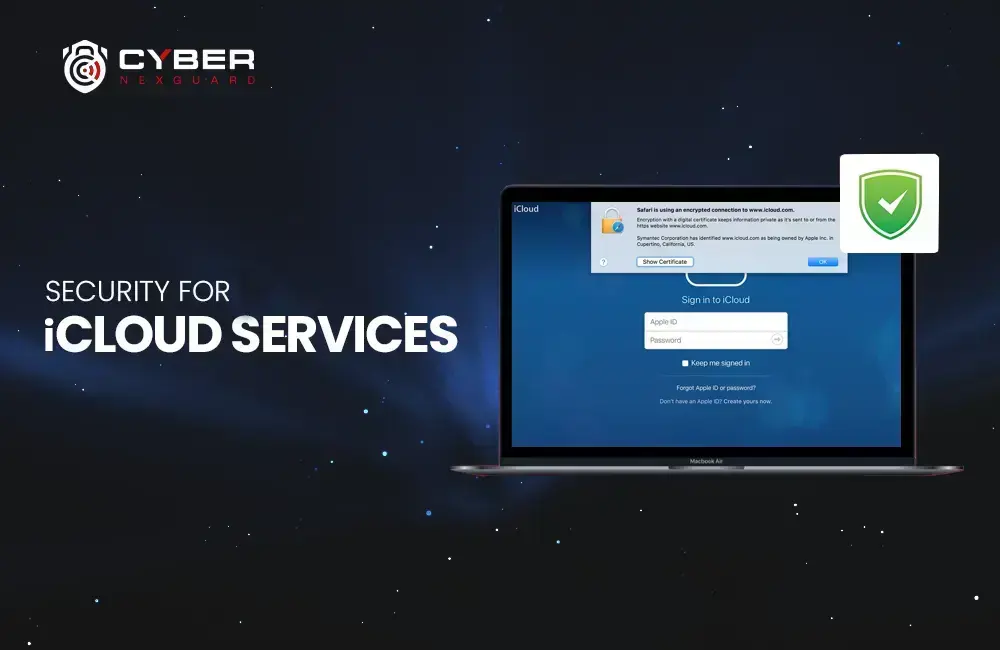
One of the most significant concerns in cloud computing is the risk of data breaches. Data stored in the cloud is susceptible to unauthorized access, and a breach can lead to sensitive information being exposed. Common causes of data breaches in the cloud vulnerabilities include weak access controls, inadequate encryption, and misconfigured security settings. Organizations must implement robust security measures to protect their data. Here is more information about vulnerabilities in 2023, which can make your data breachable.
Misconfiguration

Misconfigurations are a leading cause of vulnerabilities in cloud computing. When organizations do not properly configure their cloud services, it creates security gaps that attackers can exploit. Common misconfigurations include leaving storage buckets or databases open to the public, weak password policies, and improper firewall rules. Periodic audits and security assessments are crucial for identifying and rectifying misconfigurations.
Insider Threats
While cloud computing providers offer robust security measures, insider threats remain a significant concern. These threats can come from employees, contractors, or business partners with access to an organization’s cloud resources. Insiders may intentionally or unintentionally compromise data security. Effective identity and access management (IAM) and monitoring can help detect and mitigate insider threats.
DDoS Attacks
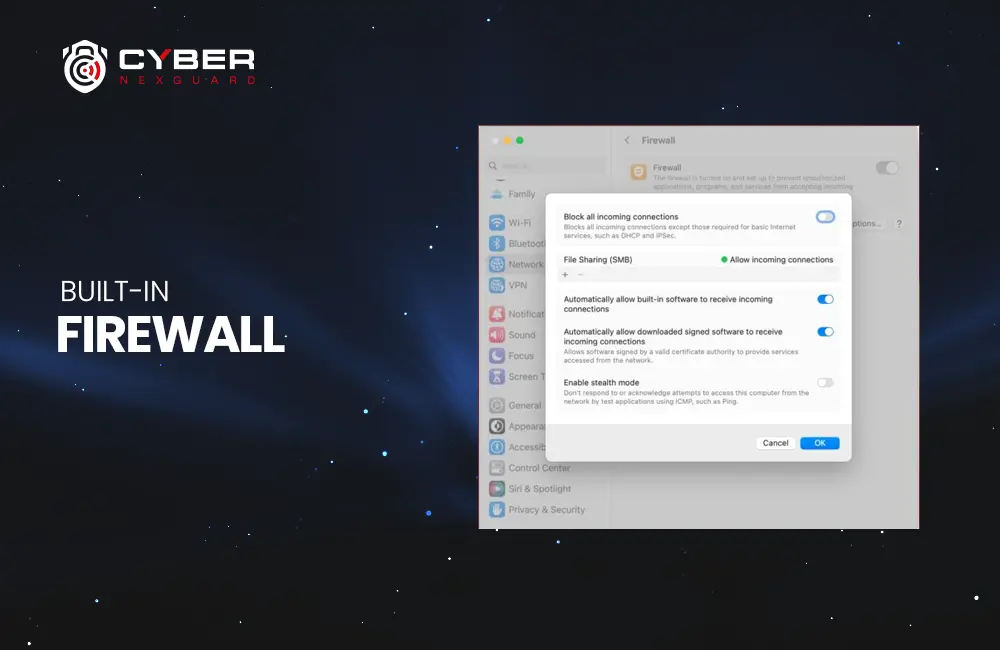
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks can overwhelm cloud resources, rendering services unavailable. Providers of cloud computing offer DDoS protection, but organizations must configure it properly to defend against attacks effectively. Failure to do so can result in service disruptions and financial losses.
Shared Responsibility Model

Security of cloud computing follows a shared responsibility model, meaning that both the cloud provider and the customer have security responsibilities. The provider is responsible for securing the underlying infrastructure, while the customer is responsible for securing their data and applications. Understanding this model is essential to avoid gaps in security coverage.
Compliance and Legal Issues
Different industries and regions have specific compliance requirements for data protection and privacy. Failing to meet these regulations can result in legal consequences and financial penalties. Customers of cloud computing must ensure that their cloud deployment adheres to relevant compliance standards.
Cloud API Security

Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) are critical components of cloud computing services, enabling communication between different cloud resources. Insecure APIs can expose vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit. Organizations should implement API security measures, including authentication and authorization mechanisms.
Cloud Provider Vulnerabilities
Even large cloud computing providers are not immune to security vulnerabilities. While they invest heavily in security, vulnerabilities can still emerge. Customers must stay informed about security patches and updates and apply them promptly to mitigate risks.
Data Loss

Data stored in the cloud can be lost due to various factors, including hardware failures, human errors, or data corruption. Organizations must implement robust data backup and recovery strategies to ensure data integrity and availability.
Shadow IT
Shadow IT refers to the use of unauthorized cloud services or applications by employees. These unapproved services can introduce security risks, as they may not adhere to the organization’s cloud computing security policies and standards. Employing cloud access security brokers (CASBs) can help organizations gain visibility and control over shadow IT. Click here if you want to get vulnerability free website or mobile application for your business.
Mitigating Vulnerabilities in Cloud Computing

To effectively mitigate vulnerabilities in cloud computing, organizations should adopt a proactive and multi-layered security approach. Here are some key strategies:
1. Security Best Practices: Implement security best practices recommended by cloud providers, including strong authentication, access controls, encryption, and regular security assessments.
2. Identity and Access Management (IAM): Implement robust IAM policies to control who has access to cloud computing resources and what actions they can perform.
3. Security Monitoring: Deploy security monitoring tools to detect and respond to threats in real-time. This includes log analysis, intrusion detection systems, and security information and event management (SIEM) solutions.
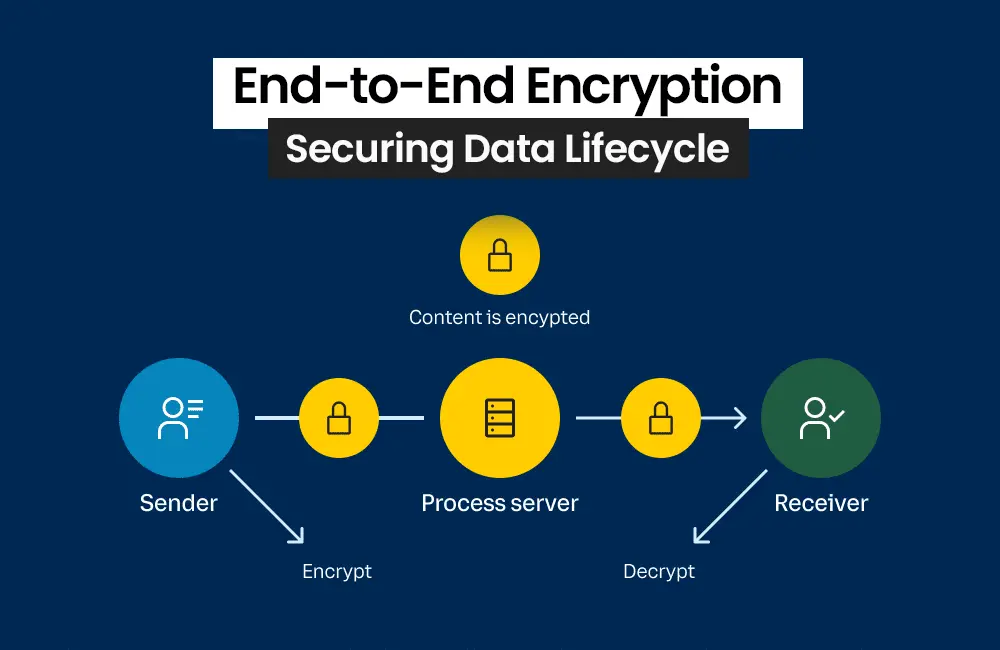
4. Data Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data both in transit and at rest. Providers of cloud computing typically offer encryption services that can be leveraged.
5. Regular Audits and Assessments: Conduct regular cloud computing security audits and assessments to identify vulnerabilities and misconfigurations. Corrective actions should be taken promptly.
6. Compliance Adherence: Ensure that your cloud deployment complies with industry-specific regulations and standards, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS.
7. Employee Training: Train employees on security of cloud computing best practices and raise awareness about the risks of insider threats and shadow IT.
8. Incident Response Plan: Develop and test an incident response plan to effectively manage and mitigate security incidents when they occur.
Conclusion
While cloud computing offers numerous benefits, organizations must be aware of the inherent vulnerabilities and security challenges that come with it. By understanding these risks and implementing robust security measures, businesses can harness the power of the cloud while safeguarding their data and applications from potential threats. Cloud security is an ongoing process, requiring vigilance and adaptation to evolving threats in the digital landscape. In this era of digital transformation, securing the cloud is not an option but a necessity for the survival and success of modern businesses.